

Wood and charcoal are bulky and fragile commodities, and the energy in woodland is thinly spread, stored in harvest-ready trees scattered throughout vast and often rugged areas. The constraint on growth was not the scarcity of wood itself after all, forests still covered over 40 percent of the dry land, and wood could be harvested sustainably because forests and coppiced woodland-stands of trees managed by periodically cutting them at their base-regenerate after they are cut down. Energy supply problems due to humanity’s reliance on wood seem to have ground progress to a halt. The cities, temples, and ships these civilizations built were not surpassed for a thousand years after the fall of the Roman Empire-even by the wealthy nation states of Renaissance Europe. Wood-based technologies were perfected by the Greeks and Romans in ancient Europe and the Han Chinese in Asia. Eventually they also used wood to prepare charcoal, burning it in furnaces to produce the materials that enabled them to develop civilizations: ceramics such as pottery, bricks, and tiles the metals bronze and iron and commodities such as salt, potash, and alum. Over thousands of years, humans also learned to use it to make fires to ward off predators, keep themselves warm, and cook their food. From the moment early hominins came down from the trees, they had used wood to make tools such as digging sticks and spears, and to make shelters.
The shift from wood to coal was an unprecedented and world-changing event. It’s useful to see how and why the transformation occurred, so that we can see how we can repeat this feat as we transition from fossil fuels back to renewables.

This energy revolution fueled economic capacity and human ingenuity, launching a 300-year-long boom we’re still enjoying today.
Use of fossil fyels in the industrail revolution free#
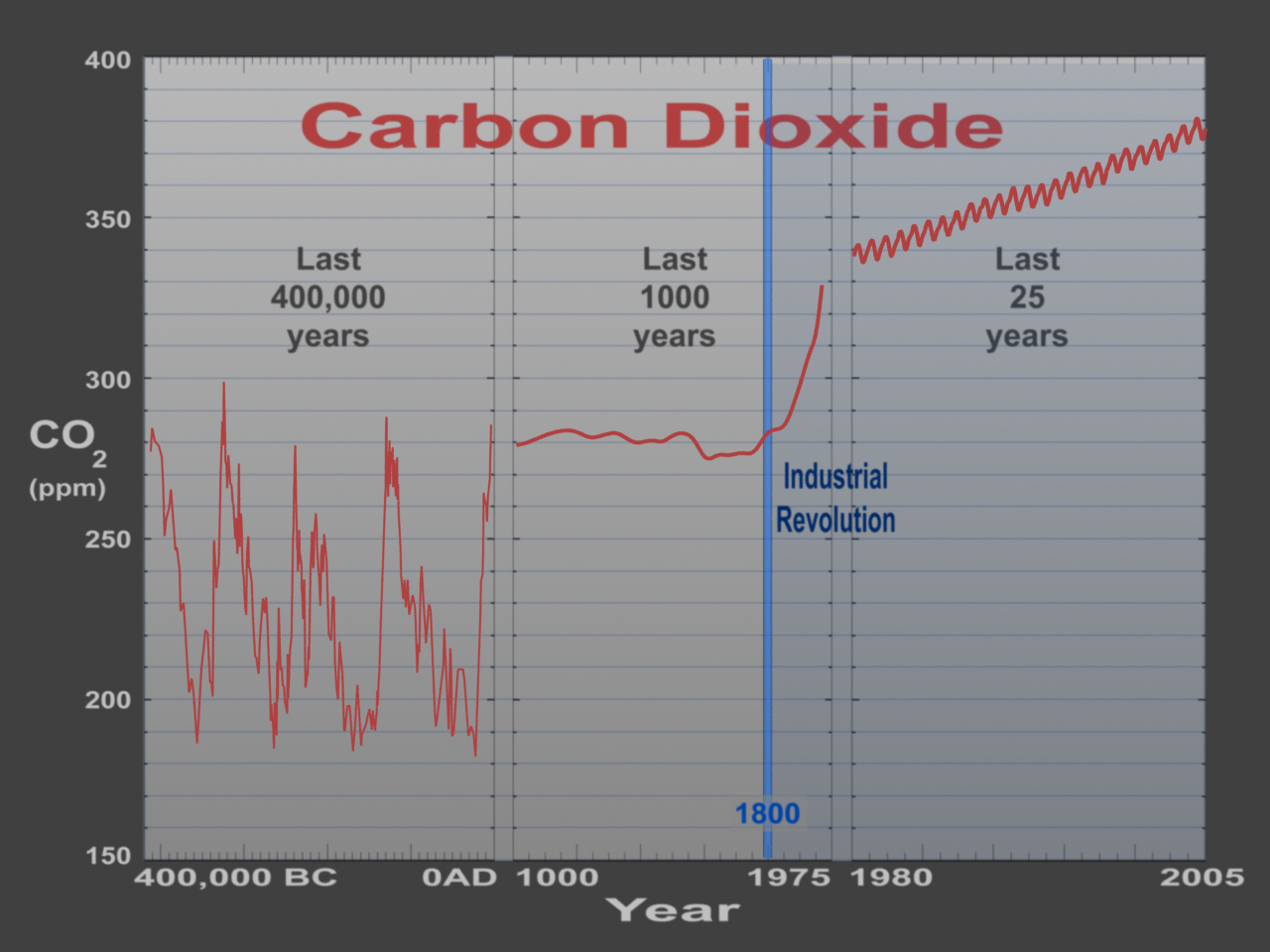
There is a lot to learn from what happened in the 16th and 17th centuries, a time when people broke free from dependence on our original energy source-wood-and started to burn our first fossil fuel-coal-instead. Politicians are being forced into action by world-wide protests, as activists push peacefully for net zero carbon emissions by 2050, which may limit global warming to 2 degrees Celsius.Īs we work to find a healthier path ahead, we might look to the past. Now, a recent spate of record heat waves, forest fires, droughts, and floods have at long last awakened the rest of the world to the immediacy of the threat from global climate change. IEEE (2003)īlankenship, R.E.: Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis.Scientists have long warned of the potential global catastrophe that burning fossil fuels could unleash on the planet. In: Power Engineering Society General Meeting, July 13-17, vol. 4. Kobayashi, K., Takano, I., Sawada, Y.: A study on a two stage maximum power point tracking control of a photovoltaic system under partially shaded insolation conditions. Solodovnik, E.V., Liu, S., Dougal, R.A.: Power Controller Design for Maximum Power Tracking in Solar Installations. International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, vol. 3, pp. Yuvarajan, S., Xu, S.: Photo-voltaic power converter with a simple maximum-powerpoint-tracker. Overall efficiency of grid connected photovoltaic inverters, European Standard EN 50530 (2010)Įsram, T., Chapman, P.L.: Comparison of Photovoltaic Array Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques. Lynn, P.A.: Electricity from Sunlight: An Introduction to Photovoltaics, p. Transactions on Industrial Electronics 53(4) (August 2006) Park, J., Ahn, J., Cho, B., Yu, G.: Dual-Module-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Control of Photovoltaic Systems. Renewable & Non-Renewable Energy sources.Reducing dependency on exhaustible natural resources Increase in usage of solar power based technologies results in. In today’s climate of growing energy needs and increasing environmental concern, alternatives to the use of non-renewable and polluting fossil fuels have to be investigated. Natural gas & Fire-wood are used for cookingĬoal & Natural Gas are used to produce Electricity Petroleum & Natural Gas are used to fuel our vehicles. Today, these are the most cheap sources of energy available for the use of both personal as well as commercial purposes. Large-scale use of fossil fuels started since the Industrial Revolution. Coal, oil and natural gas are the three different forms of fossil fuels that are widely used. Most of our present life-line systems such as cooking, Domestic electricity supply, fuels for transportation etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
